Linked List
Implementation of Singly Linked List
Now we have data type in our hand that our singly linked list is going to store.
Next we need two pointers that mark the start and end of our singly linked list. Let us declare them:
struct Node *head = NULL; struct Node *tail = NULL;
We have initialized these pointers with null to indicate that they do not hold the address of any data yet i.e. no data has been stored in the list yet.
Now we are ready to insert the data in our singly linked list. First we allocate memory to store data as:
struct Node newNode = (Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
Insertion of elements into Singly Linked List
Two cases may arise when we want to insert data at the front.
Case – 1 : When the list is empty i.e. head = NULL
Here we can simply do head = tail = newNode(pointer)
Case – 2 : When list contains some entries i.e. head != NULL
- Insertion at Front
- Insertion at End
- Insertion after a Node
Insertion of node in Linked List (Case 1)

- Before insertion, both head and tail were null pointers.
- After insertion, both head and tail are pointing to the node a .i.e. store node address of a.
Insertion of node in Linked List (Case 2a)
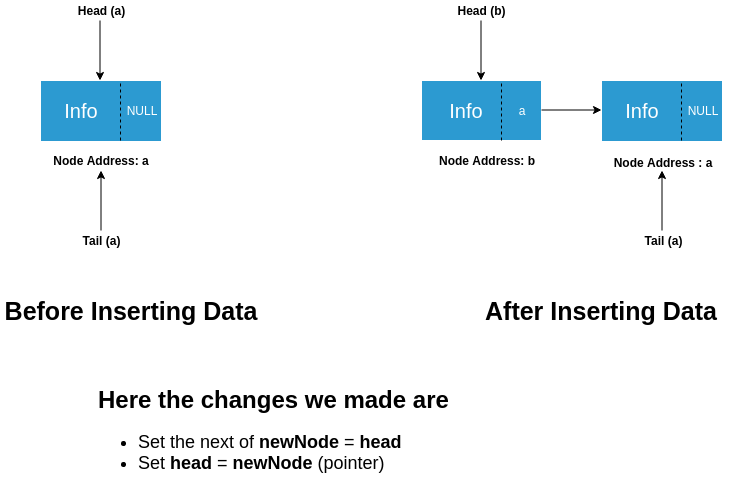
- Before insertion, both head and tail were pointing to node a.
- Since insertion is at the head hence, the head is pointing to the newnode(b) and the next of b is pointing to a. The tail will still point to a.
Insertion of node in Linked List (Case 2b)
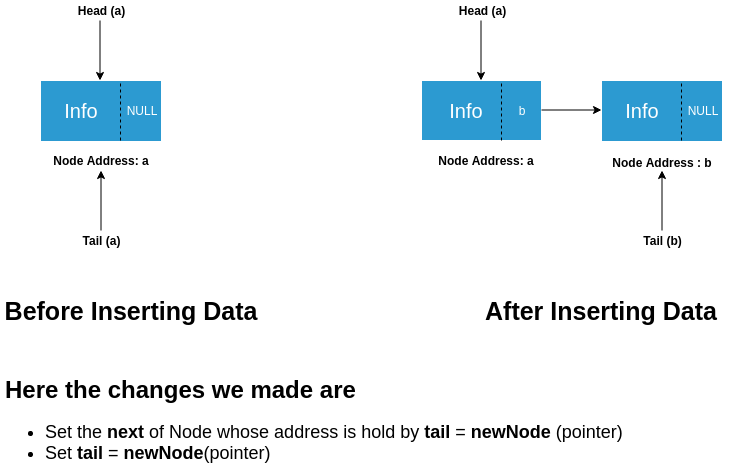
- Before insertion, both head and tail were pointing to node a.
- Since insertion is at the tail hence, the tail is pointing to the newnode(b) and the next of b is null. The head will still point to a.
Insertion of node in Linked List (Case 2c)
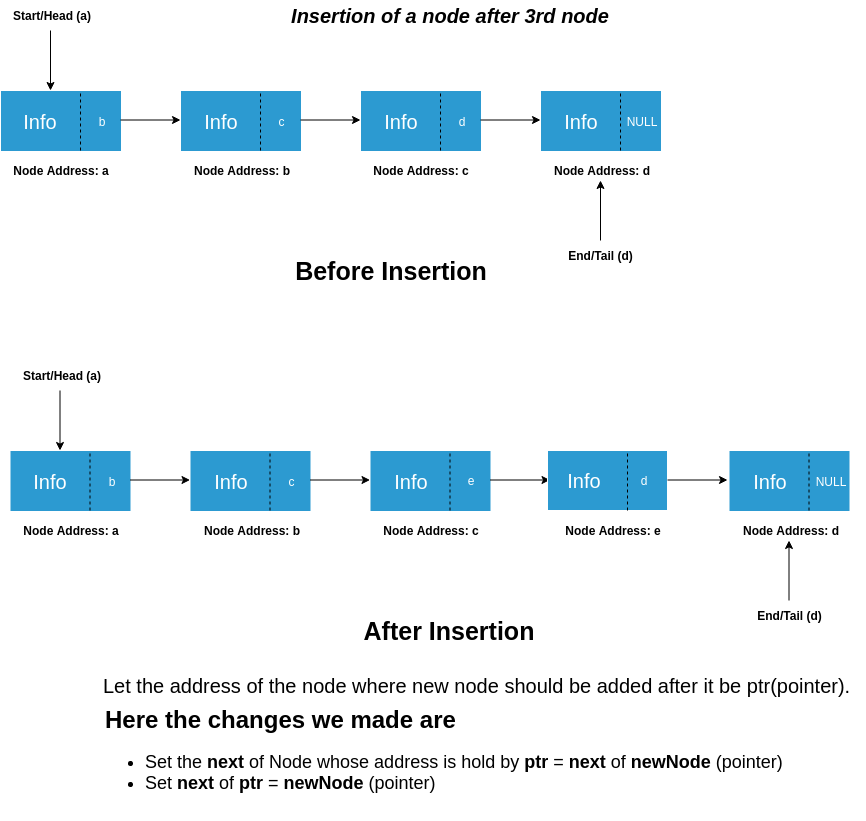
- We have inserted node e after node c in the linked list and updated the next pointers of c and e.
- The next of c which was initially pointing to d is now pointing to the newnode(e) and since, the node d has to be a part of the linked list, the next of e is pointing to d.
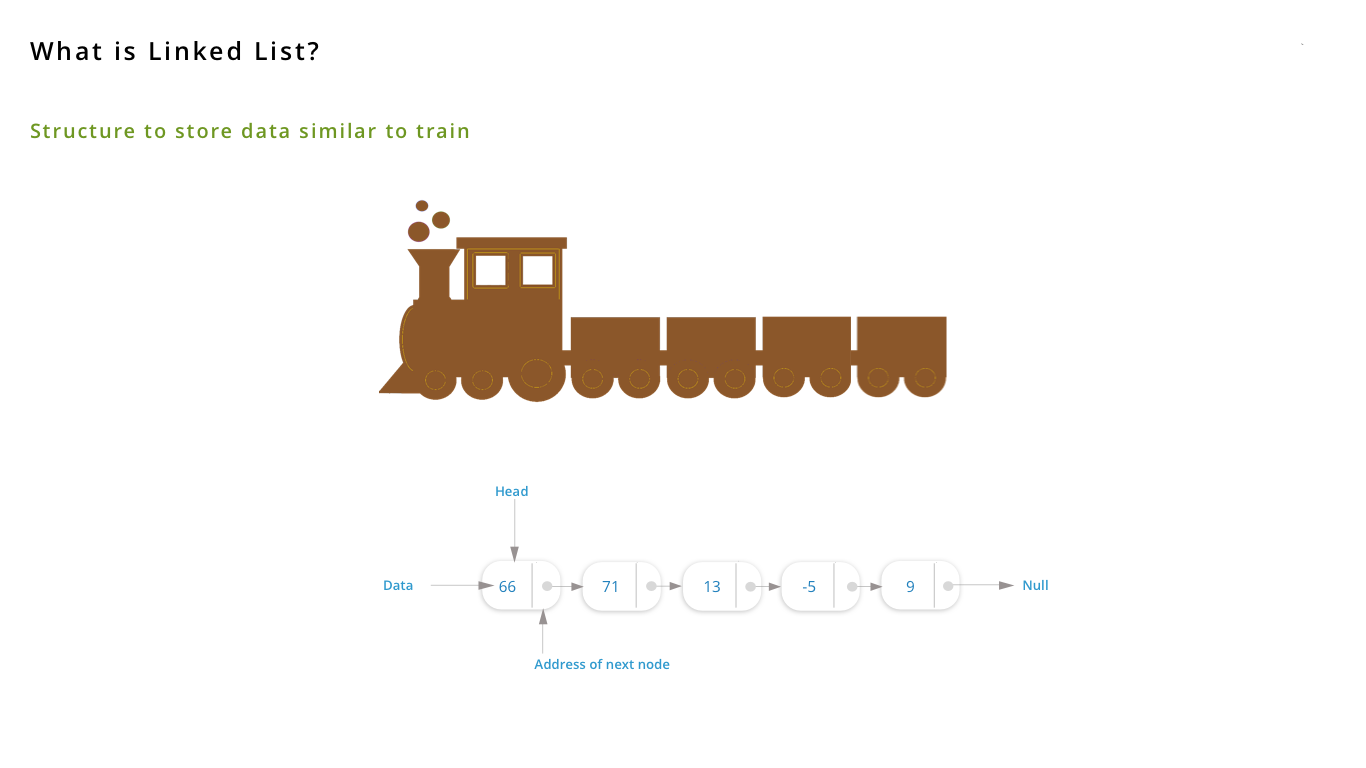
Pictorial Representation of Linked List Experiment