Breadth First Search
An Introduction to BFS Concept
Definition
- Breadth First Search (BFS) is a technique for traversing a finite graph. BFS visits the neighbour vertices before visiting the child vertices, and a queue is used in the search process. This algorithm is often used to find the shortest path from one vertex to another.
- Here we start traversing from a selected node (source node) and traverse the graph layer/level wise thus exploring the neighbour nodes (nodes which are directly connected to source node). We must move to the next layer/level only after traversing the current layer/level completely.
- In short: 1. Move horizontally and visit all the nodes of the current layer/level. 2. Move to the next layer.
An example which explains BFS
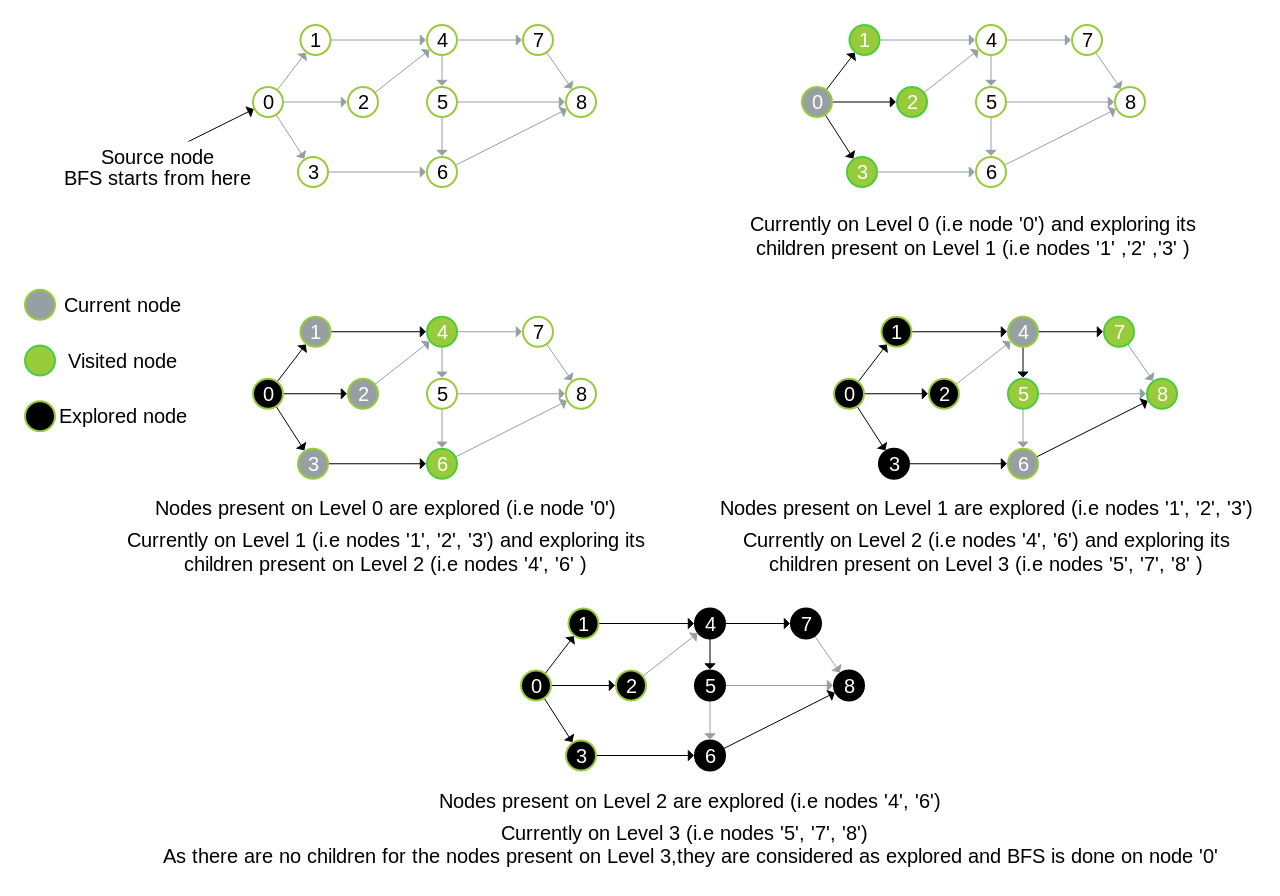
BFS Applications
Path and Minimum Spanning Tree for unweighted graph
- In an unweighted graph, the shortest path is the path with least number of edges.
- With Breadth First Search, we always reach a vertex from given source using the minimum number of edges.
- Also, in case of unweighted graphs, any spanning tree is Minimum Spanning Tree and we can use either Depth or Breadth first traversal for finding a spanning tree.
- In Peer to Peer Networks like BitTorrent, Breadth First Search is used to find all neighbour nodes.
GPS Navigation systems Breadth First Search is used to find all neighboring locations.
Cycle Detection in Undirected Graph In undirected graphs, either Breadth First Search or Depth First Search can be used to detect cycle.
In directed graph, only depth first search can be used.Finding all nodes within one connected component We can either use Breadth First or Depth First Traversal to find all nodes reachable from a given node.
